
One of the main financial statements (along with the balance sheet, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity). The income statement is also referred to as the profit and loss statement, P&L, statement of income, and the statement of operations. The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading of the statement. If a company’s https://www.bookstime.com/ stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement. Examples of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid insurance, investments, land, buildings, equipment, and goodwill.
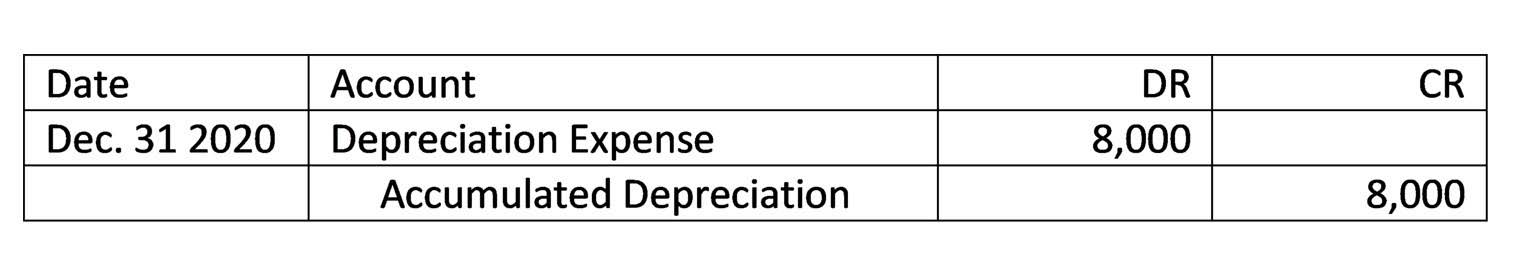
Monetary Value of Transactions

Below are some examples of transactions and how they https://x.com/BooksTimeInc affect the accounting equation. A liability is considered current of they are payable within 12 months from the end of the accounting period, or within the company’s normal operating cycle if the cycle exceeds 12 months. Obligations owed to other companies and people are considered liabilities and can be categorized as current and long-term liabilities. It includes the amount that is owed by the shareholders, as a return on their investment in the company. Shareholder’s equity includes the amount that is invested by the shareholders in the form of shares, in addition to the retained earnings that have been accumulated by the company over the course of time.

What is asset? Definition, Explanation, Types, Classification, Formula, and Measurement

By ensuring that the equation remains in balance, companies can track changes to their assets, liabilities, and equity over time and ensure the accuracy of their financial statements. The accounting equation also helps companies make informed business decisions by clearly showing their financial position and performance. The balance sheet is also known as the statement of financial position and it reflects the accounting equation. The balance sheet reports a company’s assets, liabilities, fundamental accounting equation and owner’s (or stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time. Like the accounting equation, it shows that a company’s total amount of assets equals the total amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity. The purpose of this article is to consider the fundamentals of the accounting equation and to demonstrate how it works when applied to various transactions.
- The revenue a company shareholder can claim after debts have been paid is Shareholder Equity.
- It includes the amount that is owed by the shareholders, as a return on their investment in the company.
- Thus from the above details we can understand how to do accounting equation.
- The accountants should ensure that the concept of accounting equation and its rules are properly followed and the transactions are daily and accurately recorded.
- By ensuring that the equation remains in balance, companies can track changes to their assets, liabilities, and equity over time and ensure the accuracy of their financial statements.
Understanding the Equation
In Use Journal Entries to Record Transactions and Post to T-Accounts, we add other elements to the accounting equation and expand the equation to include individual revenue and expense accounts. The accounting method under which revenues are recognized on the income statement when they are earned (rather than when the cash is received). For a company keeping accurate accounts, every business transaction will be represented in at least two of its accounts.
Implicit to the notion of a liability is the idea of an “existing” obligation to pay or perform some duty. Cash (asset) will reduce by $10 due to Anushka using the cash belonging to the business to pay for her own personal expense. As this is not really an expense of the business, Anushka is effectively being paid amounts owed to her as the owner of the business (drawings). $10,000 of cash (asset) will be received from the bank but the business must also record an equal amount representing the fact that the loan (liability) will eventually need to be repaid. Required Explain how each of the above transactions impact the accounting equation and illustrate the cumulative effect that they have.
- This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system.
- Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations.
- Hence, as of January 15, only three accounts exist with a balance – Cash, Furniture A/C, and Service Revenue (the rest get net off during the period of the whole transaction by January 15).
- This transaction affects both sides of the accounting equation; both the left and right sides of the equation increase by +$250.
- The total change on the left side is always equal to the total change on the right.
